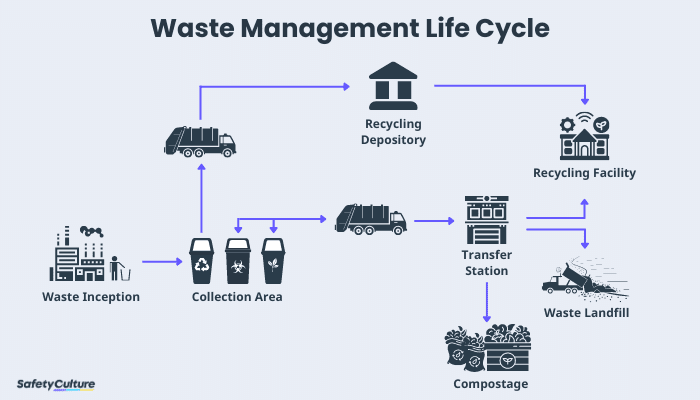
Waste management encompasses the entire process of dealing with unwanted materials, from their generation to final disposal or reuse. It involves collecting, transporting, treating, recycling, and disposing of various types of waste to minimize environmental impact and resource depletion.
Key aspects of waste management:
- Gathering waste from various sources and transporting it to treatment or disposal facilities.
- Processes like composting, recycling, incineration, or other methods to reduce waste volume and change its form.
- Converting waste materials back into usable resources, such as paper, plastic, or metal.
- Final disposal of waste materials, often through landfilling, but also including other methods like incineration or composting.
- Tracking waste streams, ensuring compliance with environmental regulations, and promoting sustainable waste management practices.
Why is waste management important?
- Minimizes pollution of air, water, and soil from improper waste disposal.
- Reduces reliance on landfilling and promotes recycling, conserving valuable resources.
- Prevents disease transmission and other health risks associated with poorly managed waste.
- Creates jobs in the recycling and waste management industries and can lead to cost savings.
Examples of waste management practices:
- Solid Waste Management: Managing household, commercial, and industrial trash.
- Liquid Waste Management: Treating and disposing of wastewater from sewage, industrial processes, and other sources.
- Hazardous Waste Management: Safely managing and disposing of dangerous materials like chemicals, medical waste, and radioactive waste.
